Conditions: Throat
Serving as part of the airway as well as the “food way,” branching to the larynx and wind-pipe as well as the middle ears, the throat lies at the crossroads of several different systems.
the throat in Breathing, snoring, and obstructive sleep apnea
Inspiration draws air to the lungs by vacuum, but the throat airway is a floppy tube that is prone to collapse. Throat airway collapse rarely happens while we are awake, but when we are asleep, our throat muscles relax significantly and a narrowing of the airway (resistance), rapid opening and closing of the airway (snoring), or longer periods of full airway blockage (including obstructive sleep apnea) can occur. This spectrum of throat airway narrowing is not only very common in the general population, but an individual is usually unaware of it happening because it occurs when they are asleep.
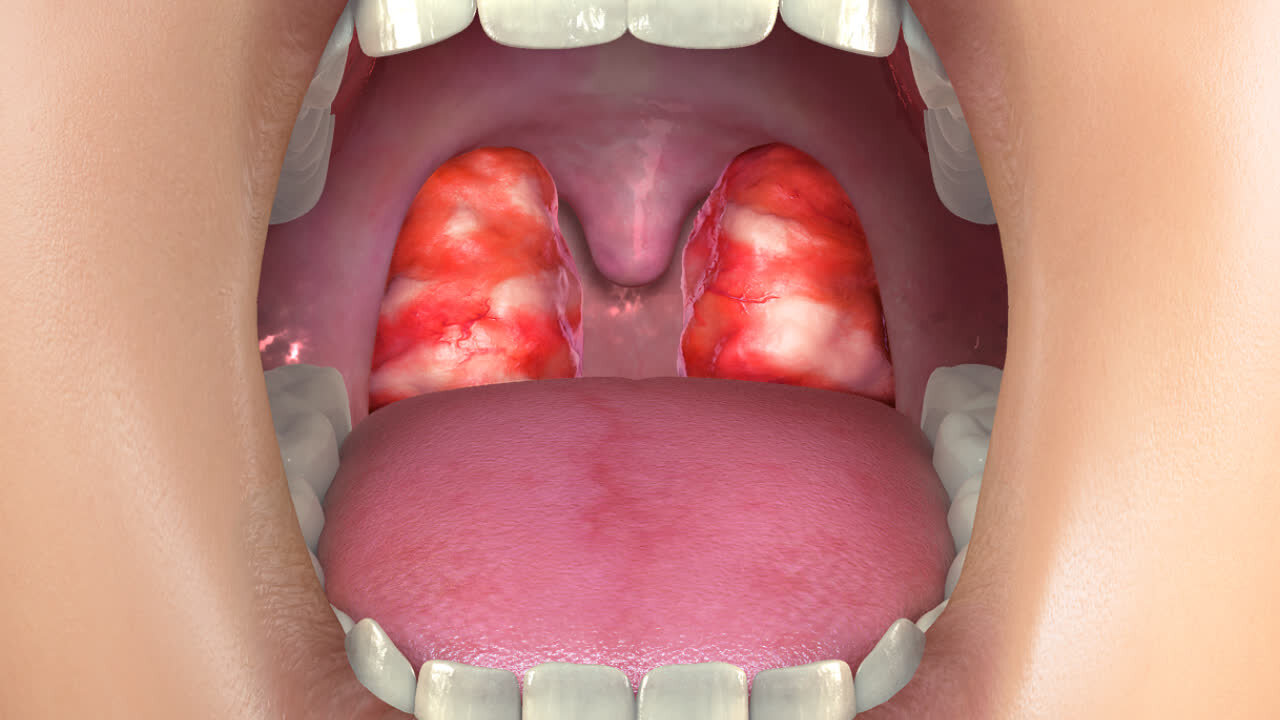
Pharyngitis (including tonsil and/or adenoid infection)
Pharyngitis means inflammation of the pharynx, typically due to infection. Most infections of the pharynx are due to viruses, and the vast majority of viral pharyngitis resolves with time. Bacterial pharyngitis left alone, may persist, and therefore treatment with an antibacterial is common. Although infection of the pharynx is often located specifically in the adenoids, tonsils, or lingual tonsils, and when this is the case, the specific terms “adenoiditis,” “tonsillitis,” or “lingual tonsillitis” may be used, the term “pharyngitis” is simply used to indicate the more general area, the pharynx, is infected.
Tonsil stones (tonsilloliths, tonsiliths)
A tonsil stone
Tonsil stones are collections of food, dead cells, and mucus that get trapped in the crypts of tonsils. They tend to harden and allow bacteria to thrive, sometimes causing tonsillitis, pain and/or bad breath. Here’s a light-hearted video explaining tonsil stones in greater detail.
Swallowing
Difficulty with swallowing can be a minor nuisance or it can be a serious condition. There are many different causes of swallowing difficulty, including from infection, stroke, throat tumor, Zenker’s diverticulum, and even the aging process. Among the more serious conditions resulting from poor swallowing include malnutrition and lung infections (aspiration pneumonia).
drainage sensation
A sensation of drainage in the throat is common, but there are different causes of this, including reflux, which is when stomach contents go back up the esophagus and irritate the throat, and less commonly sinus infection, with mucus draining down from the nose.
• Animated video explaining causes of a phlegm sensation in the throat
• Animated video explaining causes and ways to evaluate a throat foreign body sensation
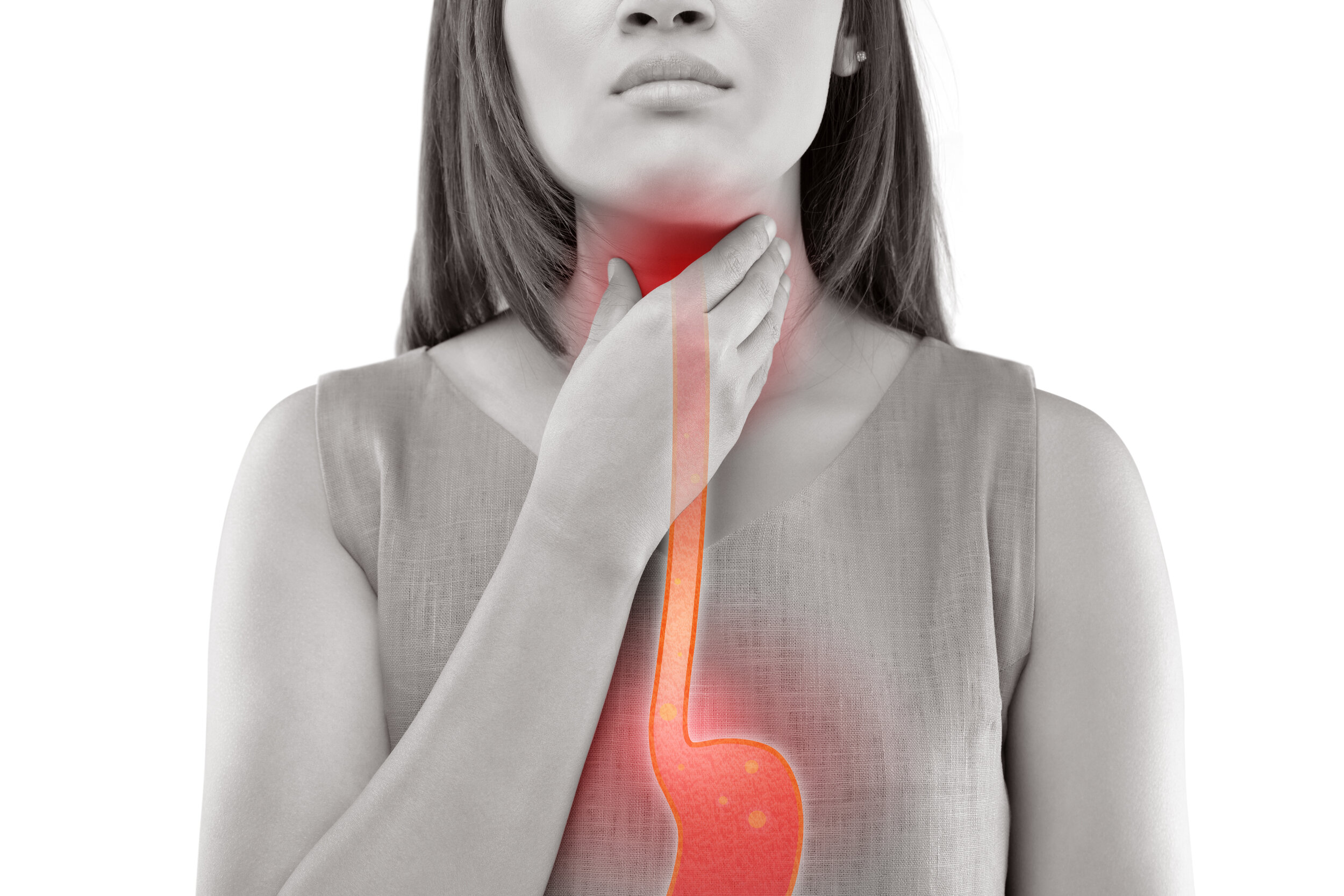
Reflux
Reflux is when stomach contents, containing acid and digestive enzymes, make their way up the esophagus. When the stomach contents make their way to the throat, a condition called laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR). Symptoms of reflux may include any of the following: heartburn, a sensation of liquid coming up to the throat (sometimes called a sour brash), frequent throat clearing, intermittent development of a gravelly voice, a sensation of post-nasal drip, as well as ear and sinus problems. Since many of these symptoms are not caused only by reflux, a given cluster of symptoms sometimes leads to suspected reflux, which may be better understood with some investigation.
Chronic cough
A cough lasting greater than eight weeks may be due to any of a long list of problems, ranging in severity from a nuisance to a lift-threatening condition.
Abscesses (including peritonsillar abscess, retropharyngeal abscess, and parapharyngeal abscess)
An abscess is a collection of infected pus. When this happens, one’s ability to resolve the infection is hindered because the pocket of pus has no blood flow within it, so the immune system cannot deliver its weapons to the center of the abscess. In the throat, a peritonsillar abscess is one between the back wall of the tonsil and the throat constricting muscles. A retropharyngeal abscess is roughly midline behind the muscles constricting the throat, and has the potential to expand downwards into the chest. A parapharyngeal abscess is in a deep pocket on a side of the neck near the carotid artery and internal jugular vein.
Throat Tumors
Many times, an enlargement or swelling in the throat is related to inflammation rather than a tumor. Tumors are uncontrolled growths of a tissue, and may be benign or malignant. Malignant (cancerous) tumors of the throat have the potential to spread to other parts of the body and can be life-threatening. Also, because of the location, tumors of the throat threaten the functions of swallowing, breathing, and talking and at times can be lethal due to blocking the airway. Fortunately, diagnosis and treatment of throat cancers has improved greatly in recent years. Evaluation involves a specialist’s examination, looking in the throat with a scope and performing a biopsy and/or imaging if needed.
how to get the most from your appointment
Appointment time is valuable. Below are some suggestions to make the most of your appointment. This preparation will help you and your doctor maximize efficiency and accuracy, freeing up time for questions and answers.
• Click here to prepare for your or your child’s tonsils/adenoids appointment.