Conditions: Otomycosis, also known as Fungal Otitis Externa
What is fungal otitis externa?
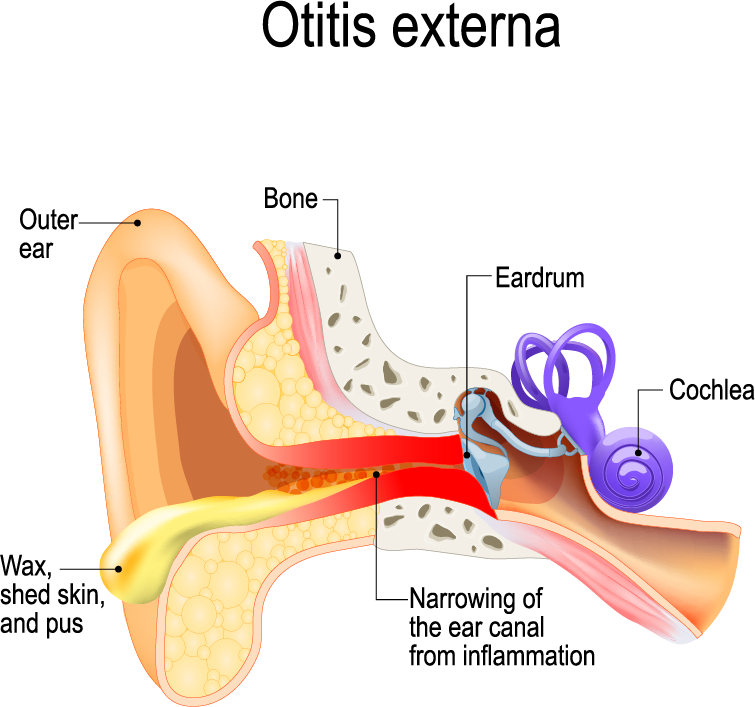
Fungal otitis externa is an infection of the ear canal with a fungus. This is different from otitis media, which is an infection deep to the eardrum. Otitis externa is not directly related to Eustachian tube dysfunction, unless Eustachian tube dysfunction has caused a perforation in the tympanic membrane.
What are the symptoms of fungal otitis externa?
Fungal otitis externa, also known as fungal ear infection or fungal swimmer's ear, may present with one or more of these symptoms:
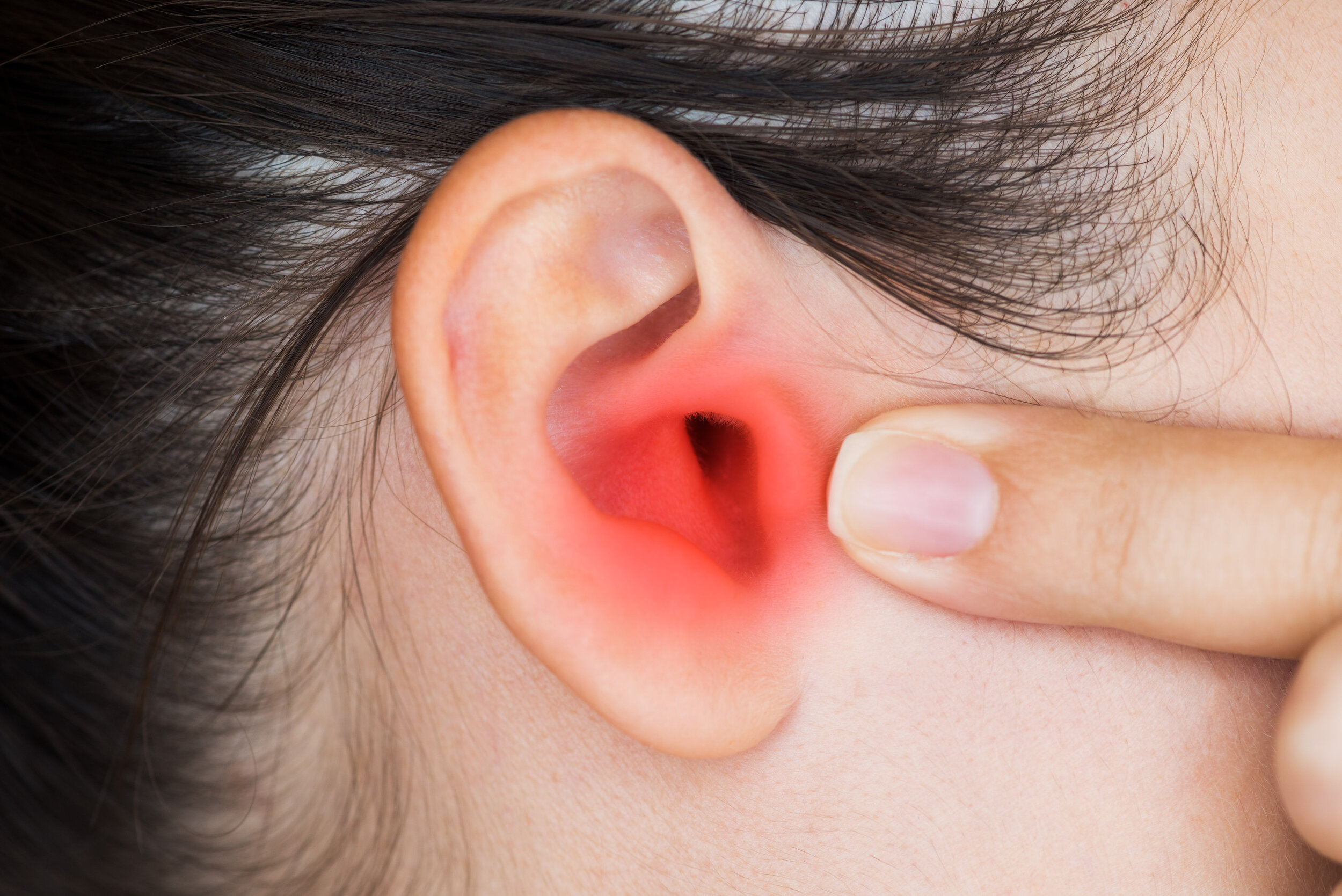
Discomfort or pain, often worsening when touching the ear or pulling on the earlobe, and sometimes extending to the area around the ear
Itching in the ear canal
Presence of a thick, white, yellow, or black discharge, sometimes described as looking like cotton or debris
A feeling of fullness or blockage in the ear
Reduced hearing due to blockage from debris or swelling
How is fungal otitis externa diagnosed?
Fungal otitis externa may be diagnosed by a physician if fungal elements are visually present. Seeing these fungal elements (hyphae or spores) is greatly facilitated with use of an ear microscope. Even when fungus is not seen, a suspicion for fungus may be raised by a whitish coloration to the discharge and/or lack of progress when an otitis externa treated with appropriate anti-bacterial antibiotics. The presence of patient factors predisposing to fungal otitis externa also raise suspicion for a fungal infection. Lastly, when diagnosis is uncertain, a swab of the drainage may be sent to the microbiology lab to be tested for the presence of fungus versus bacteria. This sample may be further tested to identify to which medications the involved organism(s) are sensitive. Often, before final laboratory information is available, a physician may begin treatment for a fungal infection and the effectiveness of this treatment may be the first confirmation of the diagnosis.
what are the types of fungi that may cause otitis externa?
The most common fungi causing otomycosis are Aspergillus niger, Aspergillus fumigatus, Penicillium and Candida albicans.
What factors predispose to fungal otitis externa?
Fungus is not “caught” or transmitted from an infected source; rather, fungus is already everywhere and will thrive when the opportunity presents. Moisture favors both bacterial and fungal otitis externa, but it is especially important in allowing fungus to thrive. Other factors predisposing to a fungal otitis externa include the following:
Recent use of antibacterial eardrops, especially those with a steroid
Weakened immune system, such as with diabetes, especially when poorly controlled, pregnancy, and use of immune-weakening drugs.
Presence of a perforation in the eardrum
History of surgery for cholesteatoma called a canal wall down mastoidectomy
Use of hearing aids or significant use of earbuds, as they trap moisture in the ear canal
Use of cotton swabs (e.g. Q-tips) or similar objects
Can the infection spread deeper?
Yes, especially in a situation of poorly controlled diabetes, but also possible in other forms of a weakened immune system, the infection may spread beyond the ear canal skin to the bone or the soft tissues deep to the skin. This condition, called necrotizing external otitis or malignant otitis externa, is more commonly due to a bacterial infection but may develop from. a fungal infection.
what are some other problems that may look like fungal otitis externa?
Bacterial otitis externa
Temporomandibular (jaw) joint dysfunction, which can cause pain in the same area
Otitis media (infection deep to the eardrum, which can cause pain, drainage, and hearing loss
Skin cancer in the ear canal, which often has an infection on the area of skin cancer, making diagnosis of cancer more difficult
Can a tympanic membrane perforation occur with fungal otitis externa?
Yes, a tympanic membrane perforation may exist prior to fungal otitis externa or may arise as a result of the fungal otitis externa. When a perforation is present prior to fungal otitis externa, moisture draining from the middle ear to the ear canal through the perforation may be the predominant predisposing factor. Alternatively, a fungal otitis externa may be the cause of a tympanic membrane perforation.
how to get the most from your EAR appointment
Appointment time is valuable. Here are some suggestions to make the most of your appointment. This preparation will help you and your doctor maximize efficiency and accuracy, freeing up time for questions and answers.
This page